| Citation: | Xiaojun Li, Wenke He, Li-Dong Zhao. Point defect engineering advances thermoelectric SnS crystals[J]. Materials Lab, 2025, 4(1): 240010. doi: 10.54227/mlab.20240010 |
Point defect engineering advances thermoelectric SnS crystals
-
Abstract
The pursuit of low-cost, high-performance thermoelectric materials is a fundamental challenge in thermoelectric research and its applications, as it can realize the direct thermal to electrical energy conversion. In the past decade, with the emergence of the hot-spot SnSe thermoelectric material, the homologous SnS has gradually gained wide attention as its lower cost and higher abundance of S. However, the highly electronegative (ionic) nature of S and the large bandgap (~ 1.2 eV) in SnS cause inherently poor electrical transport. Additionally, grain boundary in the polycrystals brings about complex defects and which further deteriorates the performance. The behavior of defects in polycrystalline SnS is difficult to clarify and modulate, but higher carrier mobility and the only point defects are considered in the crystals where factors with less influence make the identification and optimization of the transport mechanism easier. Based on it, this article proposes the improvement strategy of thermoelectric performance in SnS crystals enabled by the point defect engineering.
-
Keywords:
- SnS crystals /
- Point defect engineering
-
-
References
1. Q. Yan, M. G. Kanatzidis, Nat. Mater., 2022, 21, 503 2. B. Qin, D. Liu, Q. Cao, X. Zhang, L.-D. Zhao, Mater. Lab, 2023, 2, 230029 3. X. L. Shi, J. Zou, Z. G. Chen, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 7399 4. D. L. Zhao, G. Tan, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2014, 66, 15 5. J. Mao, G. Chen, Z. F. Ren, Nat. Mater., 2021, 20, 454 6. W. Liu, S. Bai, J. Materiomics, 2019, 5, 321 7. Q. Zhu, S. Wang, X. Wang, A. Suwardi, M. H. Chua, X. Y. D. Soo, J. Xu, Nano-Micro Lett., 2021, 13, 119 8. G. Tan, L.-D. Zhao, M. G. Kanatzidis, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 12123 9. J. Sun, Y. Zhang, Y. Fan, X. Tang, G. Tan, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 431, 133699 10. Z. Liu, W. Gao, F. Guo, W. Cai, Q. Zhang, J. Sui, Mater. Lab, 2022, 1, 220003 11. X. Tang, Z. Li, W. Liu, Q. Zhang, C. Uher, Interdiscip Mater., 2022, 1, 88 12. Z. Liu, T. Hong, L. Xu, S. Wang, X. Gao, C. Chang, X. Ding, Y. Xiao, L.-D. Zhao, Interdiscip Mater., 2023, 2, 161 13. B. Qin, L. -D. Zhao, Mater. Lab, 2022, 1, 220004 14. F. Zhang, D. Wu, J. He, Mater. Lab, 2022, 1, 220012 15. C. Fu, H. Wu, Y. Liu, J. He, X. Zhao, T. Zhu, Adv. Sci., 2016, 3, 1600035 16. J. He, T. M. Tritt, Science, 2017, 357, eaak9997 17. L.-D. Zhao, S. H. Lo, Y. Zhang, H. Sun, G. Tan, C. Uher, C. Wolverton, V. P. Dravid, M. G. Kanatzidis, Nature, 2014, 508, 373 18. J. Jiang, Y. Pan, T. Zhou, Y. Niu, X. Kong, J. Song, C. Yang, Y. Yu, C. Wang, Mater. Today Commun., 2020, 24, 101167 19. D. Liu, B. Qin, L.-D. Zhao, Mater. Lab, 2022, 1, 220006 20. Y. Hu, S. Bai, Y. Wen, D. Liu, T. Hong, S. Liu, S. Zhan, T. Gao, P. Chen, Y. Li, L. Wang, D. Gao, X. Gao, Q. Tan, B. Qin, L.-D. Zhao, Adv. Funct. Mater, 2025, 35, 2414881 21. Z. Wang, D. Wang, Y. Qiu, J. He, L.-D. Zhao, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 789, 485 22. W. He, D. Wang, H. Wu, Y. Xiao, Y. Zhang, D. He, Y. Feng, Y.-J. Hao, J.-F. Dong, R. Chetty, L. Hao, D. Chen, J. Qin, Q. Yang, X. Li, J.-M. Song, Y. Zhu, W. Xu, C. Niu, X. Li, G. Wang, C. Liu, M. Ohta, S. J. Pennycook, J. He, J.-F. Li, L.-D. Zhao, Science, 2019, 365, 1418 23. Z. He, J. Zhu, W. Su, X. An, C. Zhao, W. Yuan, L. Lin, R. Ang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2023, 123, 242104 24. Asfandiyar, W. Xue, J. Mao, K. Liu, Q. Zhang, J.-F. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16, 38073 25. Asfandiyar, B. Cai, L.-D. Zhao, J.-F. Li, J. Materiomics, 2020, 6, 77 26. H. Wu, K. Peng, B. Zhang, X. N. Gong, Z. Z. Feng, X. M. Zhang, M. Xi, X. M. Yan, Y. S. Zhang, G. Y. Wang, X. Lu, X. Y. Zhou, Mater. Today Phys., 2020, 14, 100221 27. W. He, B. Qin, L.-D. Zhao, Chin. Phys. Lett., 2020, 37, 087104 28. W. He, D. Wang, J.-F. Dong, Y. Qiu, L. Fu, Y. Feng, Y. Hao, G. Wang, J. Wang, C. Liu, J.-F. Li, J. He, L.-D. Zhao, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 10048 29. H. Wu, X. Lu, G. Wang, K. Peng, H. Chi, B. Zhang, Y. Chen, C. Li, Y. Yan, L. Guo, C. Uher, X. Zhou, X. Han, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1800087 30. W. He, R. Ang, L.-D. Zhao, Sci. China Mater., 2022, 65, 1143 31. Q. Tan, L.-D. Zhao, J.-F. Li, C.-F. Wu, T.-R. Wei, Z.-B. Xing, M. G. Kanatzidis, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 17302 32. Q. Tan, C.-F. Wu, W. Sun, J.-F. Li, RSC Advances, 2016, 6, 43985 33. Y. Niu, Y. Chen, J. Jiang, Y. Pan, C. Yang, C. Wang, IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2020, 738, 012016 34. L.-D. Zhao, G. Tan, S. Hao, J. He, Y. Pei, H. Chi, H. Wang, S. Gong, H. Xu, V. P. Dravid, C. Uher, G. J. Snyder, C. Wolverton, M. G. Kanatzidis, Science, 2016, 351, 141 35. C. Chang, M. Wu, D. He, Y. Pei, C.-F. Wu, X. Wu, H. Yu, F. Zhu, K. Wang, Y. Chen, L. Huang, J.-F. Li, J. He, L.-D. Zhao, Science, 2018, 360, 778 36. J. P. Heremans, V. Jovovic, E. S. Toberer, A. Saramat, K. Kurosaki, A. Charoenphakdee, S. Yamanaka, G. J. Snyder, Science, 2008, 321, 554 37. K. Biswas, J. He, Q. Zhang, G. Wang, C. Uher, V. P. Dravid, M. G. Kanatzidis, Nat. Chem., 2011, 3, 160 38. S. Wang, G. Zheng, T. Luo, X. She, H. Li, X. Tang, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2011, 44, 475304 39. Y. Qin, T. Hong, B. Qin, D. Wang, W. He, X. Gao, Y. Xiao, L. -D. Zhao, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2102185 40. G. J. Snyder, A. H. Snyder, M. Wood, R. Gurunathan, B. H. Snyder, C. Niu, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2001537 41. R. Guo, X. Wang, Y. Kuang, B. Huang, Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 92, 115202 42. O. Delaire, J. Ma, K. Marty, A. F. May, M. A. McGuire, M. H. Du, D. J. Singh, A. Podlesnyak, G. Ehlers, M. D. Lumsden, B. C. Sales, Nat. Mater., 2011, 10, 614 -
Rights and permissions
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Information
Article Metrics
-
Figure 1.
Point defect engineering in SnS crystals.
-
Figure 2.
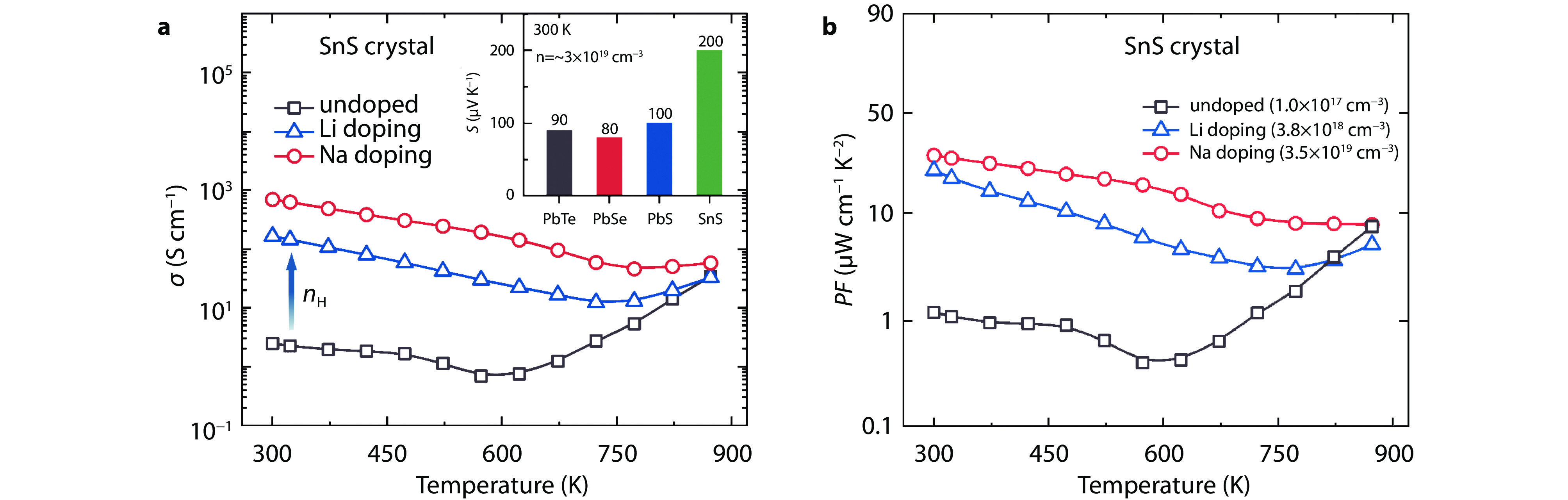
Electrical transport properties for undoped, Li and Na doped SnS crystals. a Electrical conductivity, inset shows Seebeck coefficients of group IV-VI thermoelectric compounds at a carrier concentration of ~ 3 × 1019 cm−3.[37–39] b Power factor.[28]
-
Figure 3.
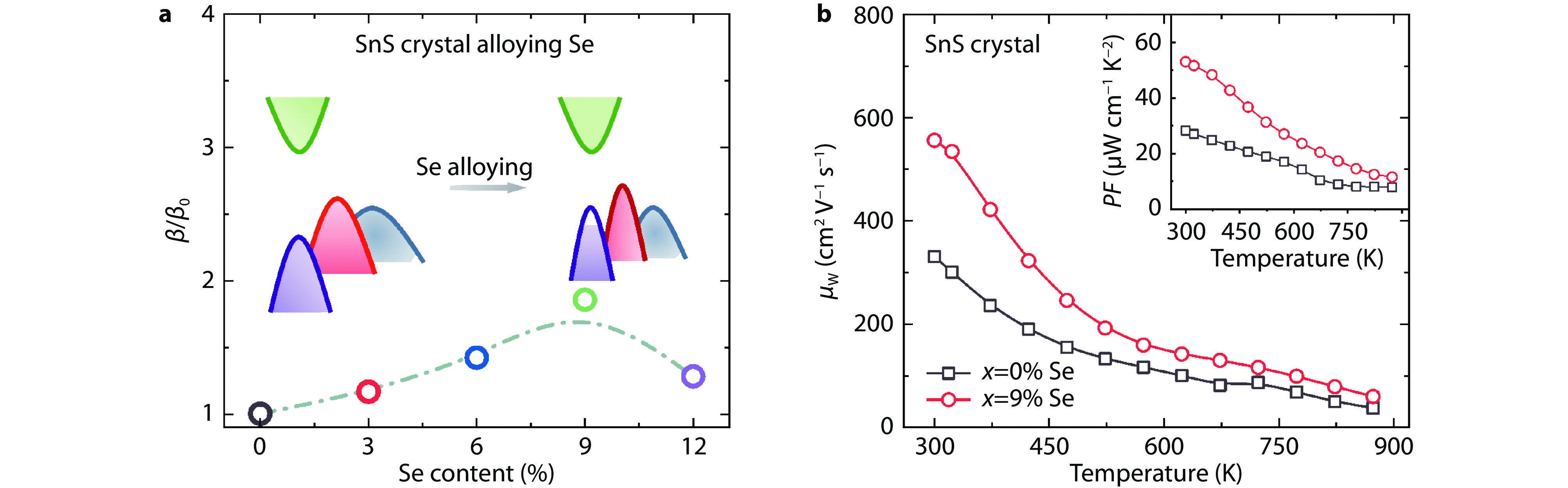
Electrical transport properties in SnS1-xSex (x = 0-9%) crystals. a The ratio of quality factor (β/β0). b Weighted mobility and power factor.[22]
-
Figure 4.
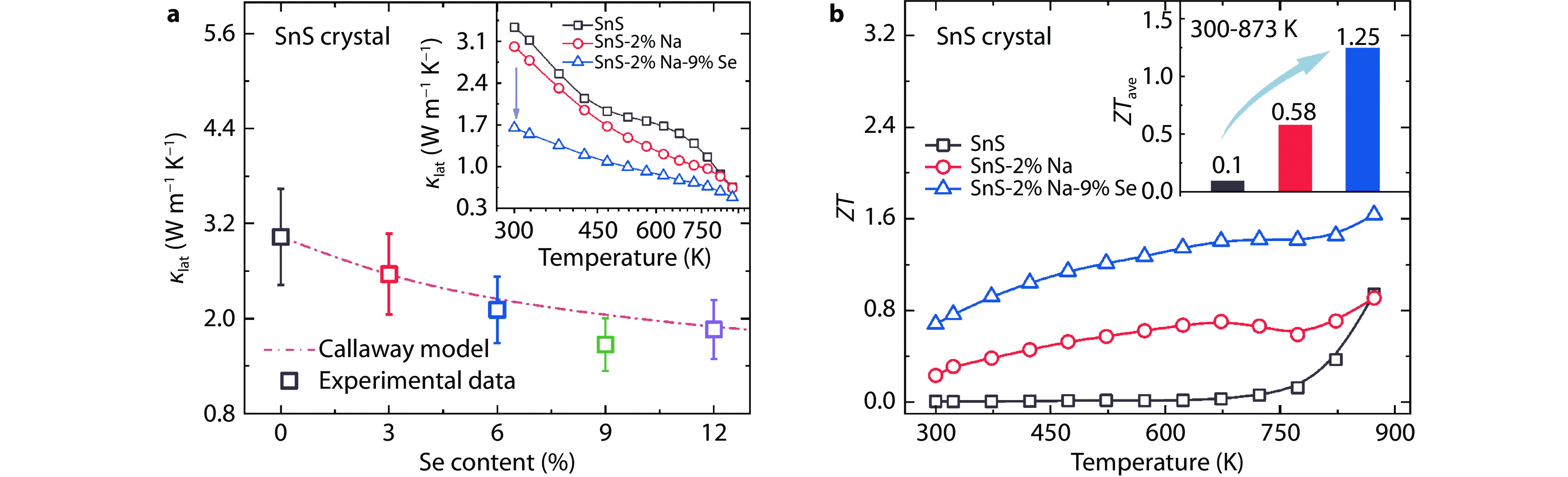
Thermal transport properties for SnS-based crystals. a Lattice thermal conductivities with fitted Callaway model at room temperature, inset shows the temperature dependent lattice thermal conductivity. b ZT and ZTave values.[22]
 Xiaojun Li received his master’s degree from Shaanxi Normal University, China, in 2023. He is now a Ph.D. candidate at the Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. His research focuses on the thermoelectric properties of SnS crystals.
Xiaojun Li received his master’s degree from Shaanxi Normal University, China, in 2023. He is now a Ph.D. candidate at the Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. His research focuses on the thermoelectric properties of SnS crystals.  Wenke He is currently a research fellow at the Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. He received his BE degree from China Three Gorges University in 2016 and PhD degree from Beihang University in 2021. His main research interests focus on the crystal growth and performance optimization of thermoelectric materials with layered structures.
Wenke He is currently a research fellow at the Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. He received his BE degree from China Three Gorges University in 2016 and PhD degree from Beihang University in 2021. His main research interests focus on the crystal growth and performance optimization of thermoelectric materials with layered structures.  Li-Dong Zhao is currently a full professor of the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Beihang University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree from the University of Science and Technology Beijing, China in 2009. He was a postdoctoral research associate at the Université Paris-Sud and Northwestern University from 2009 to 2014. His research interests include electrical and thermal transport behaviors in the compounds with layered structures. He has authored over 270 peer-reviewed publications in international journals with an h-index of 87. Professor Zhao has been identified as Highly Cited Researchers by Clarivate (2019-2024).
Li-Dong Zhao is currently a full professor of the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Beihang University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree from the University of Science and Technology Beijing, China in 2009. He was a postdoctoral research associate at the Université Paris-Sud and Northwestern University from 2009 to 2014. His research interests include electrical and thermal transport behaviors in the compounds with layered structures. He has authored over 270 peer-reviewed publications in international journals with an h-index of 87. Professor Zhao has been identified as Highly Cited Researchers by Clarivate (2019-2024). 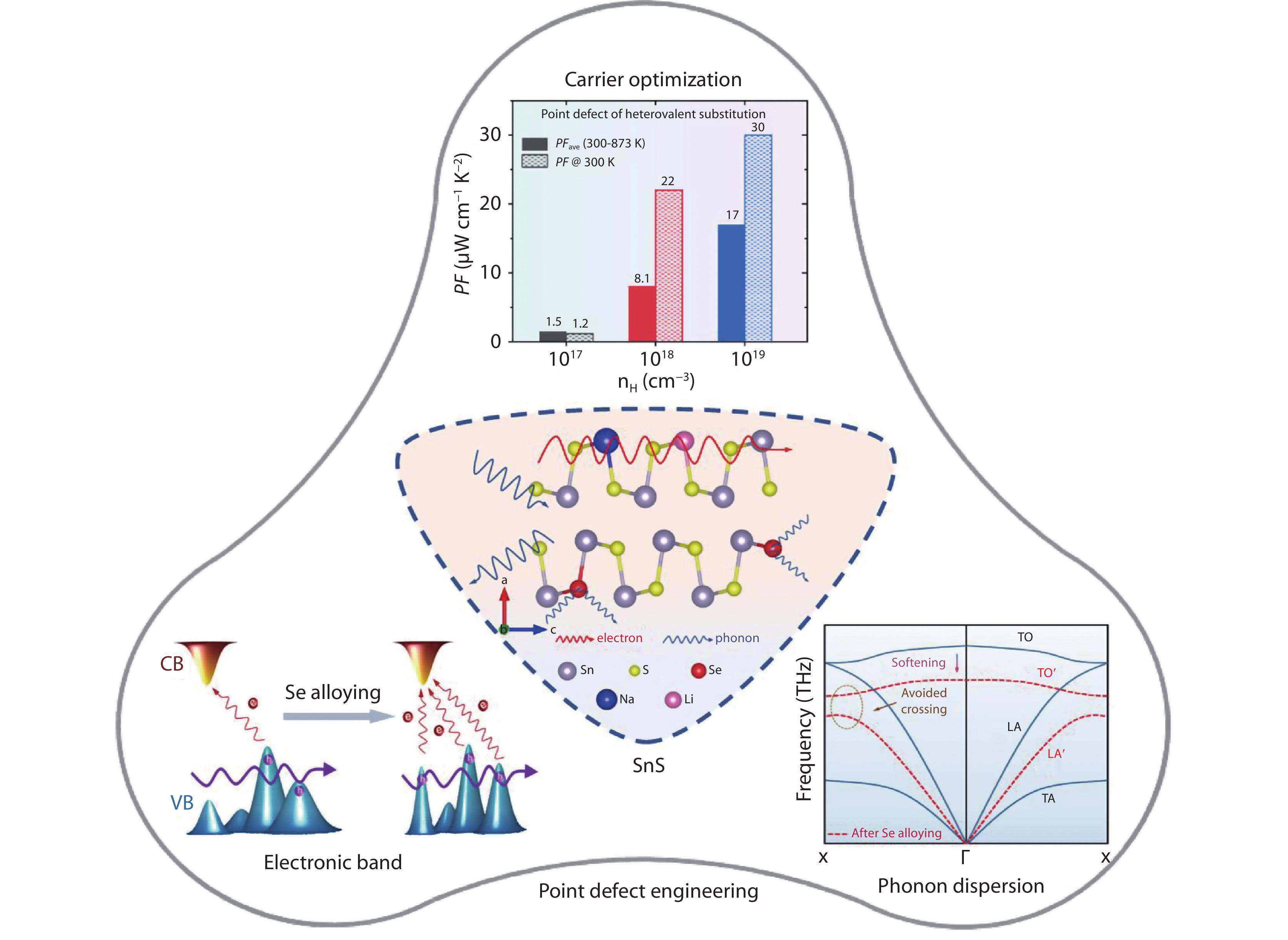

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: